Enhancing Digital Experiences: The Power of User Experience Design
User Experience Design: Creating Seamless Digital Experiences for Users
In today’s digital age, user experience (UX) design has become a critical component of building successful websites, apps, and digital products. It is the art and science of creating intuitive, engaging, and seamless experiences that delight users and keep them coming back for more.
At its core, UX design focuses on understanding the needs, behaviors, and preferences of users to create interfaces that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional. It involves meticulous planning, research, and testing to ensure that every interaction a user has with a product is smooth and effortless.
A well-designed user experience goes beyond just aesthetics. It considers factors such as ease of navigation, clear information hierarchy, efficient task completion, and responsive design across various devices. By putting users at the center of the design process, UX designers aim to remove any barriers or frustrations that might hinder their journey through a digital interface.
One key aspect of UX design is usability testing. This involves observing real users as they interact with a prototype or an existing product to identify pain points or areas for improvement. By gathering feedback early in the design process, designers can make informed decisions that enhance the overall user experience.
Another crucial element of UX design is empathy. Understanding the motivations and goals of users allows designers to create experiences that resonate with their needs. This involves conducting user research through surveys, interviews, and data analysis to gain insights into user behavior patterns.
Moreover, UX designers employ various techniques such as wireframing and prototyping to visualize the structure and flow of a product before it is developed. These tools help refine the design iteratively based on feedback from stakeholders and end-users.
In recent years, mobile responsiveness has become increasingly important in UX design. With the proliferation of smartphones and tablets, designing for multiple screen sizes has become essential to ensure a consistent experience across devices.
Furthermore, accessibility is another vital consideration in UX design. Designers must ensure that their products are accessible to users with disabilities, such as providing alternative text for images, using appropriate color contrasts, and incorporating assistive technologies.
Ultimately, UX design is a continuous process that requires ongoing evaluation and improvement. As technology advances and user expectations evolve, it is crucial for designers to stay updated with the latest trends and best practices in order to deliver exceptional user experiences.
In conclusion, user experience design plays a pivotal role in creating digital products that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive and functional. By putting users at the heart of the design process, UX designers can create seamless experiences that leave a lasting impression. With a focus on usability, empathy, and continuous improvement, UX design ensures that every interaction with a digital interface is enjoyable and engaging for users.
9 Essential FAQs About User Experience Design: Everything You Need to Know
- What is user experience (UX) design?
- How do I become a UX designer?
- What skills are needed for UX design?
- How does UX design improve customer experience?
- What tools are used in UX design?
- What is the difference between UI and UX design?
- How can I measure the success of my UX designs?
- How do I create a good user experience on mobile devices?
- What trends should I be aware of when it comes to UX design?
What is user experience (UX) design?
User Experience (UX) design refers to the process of enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and overall interaction between users and a product or system. It encompasses all aspects of a user’s experience, including their emotions, perceptions, and behaviors when interacting with a digital interface.
UX design focuses on creating meaningful and enjoyable experiences for users by understanding their needs, goals, and preferences. It involves a multidisciplinary approach that combines elements of psychology, design thinking, information architecture, visual design, and usability testing.
The goal of UX design is to create intuitive and seamless experiences that meet user expectations and provide value. It involves designing interfaces that are easy to navigate, visually appealing, and efficient in helping users accomplish their tasks. UX designers strive to remove any barriers or frustrations that might hinder users from achieving their goals.
To achieve this, UX designers conduct extensive research to gain insights into user behavior patterns. They employ techniques such as user interviews, surveys, personas creation, and usability testing to understand user motivations and pain points. This research informs the design decisions made throughout the process.
UX designers also utilize various tools and methods like wireframing, prototyping, information architecture planning, and interaction design to visualize the structure and flow of a product before it is developed. By creating interactive prototypes or mockups early on in the process, designers can gather feedback from stakeholders and end-users to iterate on the design.
Accessibility is another critical aspect of UX design. Designers ensure that their products are inclusive and accessible to users with disabilities by following accessibility guidelines such as providing alternative text for images or using appropriate color contrasts.
In summary, UX design is a holistic approach that focuses on creating positive experiences for users when interacting with digital products or systems. By considering usability principles, conducting research on user needs, prototyping designs iteratively based on feedback, and ensuring accessibility standards are met; UX designers aim to deliver products that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to use.
How do I become a UX designer?
Becoming a UX designer requires a combination of skills, knowledge, and practical experience. Here are some steps you can take to start your journey towards becoming a UX designer:
- Educate Yourself: Begin by learning about the principles and concepts of user experience design. There are numerous online resources, books, and courses available that can help you understand the fundamentals of UX design. Familiarize yourself with topics such as usability, information architecture, interaction design, and visual design.
- Gain Knowledge in Related Fields: UX design is an interdisciplinary field that intersects with areas such as psychology, anthropology, and human-computer interaction. Expand your knowledge in these fields to gain a deeper understanding of user behavior and motivations.
- Build a Strong Foundation in Design: Develop skills in visual design, typography, color theory, and layout principles. Understanding these fundamental design principles will help you create aesthetically pleasing interfaces that enhance the overall user experience.
- Practice UI Design Skills: User interface (UI) design is closely related to UX design. Familiarize yourself with UI design tools such as Sketch or Adobe XD and practice creating visually appealing interfaces.
- Learn Prototyping Tools: Prototyping tools like InVision or Figma allow you to create interactive prototypes that simulate the user experience. Mastering these tools will enable you to test and validate your designs before development.
- Gain Practical Experience: Look for opportunities to gain hands-on experience in UX design. This could involve working on personal projects or collaborating with others on real-world projects. Building a portfolio showcasing your work will be valuable when applying for jobs or freelance opportunities.
- Network and Collaborate: Connect with other professionals in the field through networking events or online communities dedicated to UX design. Collaborating with others can provide valuable insights and help you grow as a designer.
- Stay Updated: The field of UX design is constantly evolving with new techniques, tools, and trends. Stay updated by reading industry blogs, attending webinars, and participating in workshops or conferences.
- Seek Feedback: Solicit feedback on your designs from peers, mentors, or potential users. Constructive criticism can help you identify areas for improvement and refine your skills.
- Pursue Formal Education or Certification: While not always necessary, obtaining a degree or certification in UX design can provide a solid foundation and make you more competitive in the job market.
Remember, becoming a UX designer is a continuous learning process. Embrace opportunities to learn, grow, and adapt as the field evolves. With dedication, practice, and a passion for creating exceptional user experiences, you can embark on a rewarding career as a UX designer.
What skills are needed for UX design?
UX design requires a combination of technical, creative, and interpersonal skills. Here are some essential skills needed for a successful career in UX design:
- User Research: The ability to conduct user research through interviews, surveys, and data analysis to understand user needs, behaviors, and motivations.
- Information Architecture: Proficiency in organizing and structuring information in a logical and intuitive way to ensure easy navigation and findability within a digital product.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Skill in creating wireframes and prototypes using tools like Sketch, Adobe XD, or Figma to visualize the layout, structure, and interactions of a digital product.
- Usability Testing: The capability to plan and conduct usability tests with real users to gather feedback on the usability and effectiveness of a product’s design.
- Visual Design: A solid understanding of visual design principles such as typography, color theory, layout composition, and graphic design tools like Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator.
- Interaction Design: Proficiency in designing intuitive interactions that guide users through a digital interface seamlessly while considering factors like affordance, feedback, and responsiveness.
- UI Design: Knowledge of user interface (UI) design principles to create visually appealing interfaces that align with the brand’s identity while maintaining consistency across different screens.
- Collaboration: The ability to work effectively with cross-functional teams such as developers, product managers, marketers, and stakeholders throughout the design process.
- Analytical Skills: Proficiency in analyzing data from user research or usability testing to identify trends, patterns, and insights that inform design decisions.
- Communication Skills: Strong verbal and written communication skills are essential for presenting ideas effectively to team members or stakeholders and advocating for user-centered design principles.
- Empathy: The capacity to empathize with users’ needs and frustrations to create experiences that address their pain points effectively.
- Adaptability: A willingness to learn new tools, techniques, and design trends as the UX field continues to evolve rapidly.
Remember, while these skills are important, it’s also crucial to continuously learn and adapt to new technologies and user expectations to stay at the forefront of UX design.
How does UX design improve customer experience?
UX design plays a crucial role in improving customer experience by focusing on creating intuitive, user-friendly, and enjoyable interactions with digital products. Here are some ways UX design enhances customer experience:
- Ease of Use: UX designers strive to simplify complex processes and make them more accessible to users. By streamlining navigation, minimizing the number of steps required to complete tasks, and providing clear instructions, UX design ensures that customers can easily accomplish their goals without frustration or confusion.
- Intuitive Interfaces: A well-designed user interface anticipates user needs and provides intuitive interactions. Through thoughtful placement of elements, logical information hierarchy, and familiar design patterns, UX designers create interfaces that feel natural to users, reducing the learning curve and enhancing the overall experience.
- Consistency: Consistency is key in UX design. By maintaining a consistent visual style, layout, and interaction patterns throughout a digital product, customers can easily navigate different sections or features without feeling disoriented. This consistency builds trust and familiarity with the product over time.
- Personalization: UX design allows for personalized experiences tailored to individual customer preferences. By understanding user behavior through data analysis and incorporating personalization features such as recommended content or customized settings, UX designers can create experiences that feel tailored specifically for each customer.
- Speed and Performance: Customers expect fast-loading websites and responsive applications. UX designers optimize performance by reducing load times, optimizing images and code, and ensuring smooth transitions between screens or pages. Improved speed enhances customer satisfaction by minimizing waiting times and enabling swift interactions.
- Accessibility: Accessibility is an essential aspect of UX design that ensures all customers can access digital products regardless of disabilities or impairments. By following accessibility guidelines and incorporating features such as screen reader compatibility or keyboard navigation options, UX designers make sure that every customer can engage with the product effectively.
- Emotional Connection: Effective UX design considers not only functional aspects but also emotional aspects of the user experience. By creating visually appealing designs, using appropriate colors and typography, and evoking positive emotions through interactions, UX designers can forge an emotional connection between the customer and the product, enhancing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Continuous Improvement: UX design is an iterative process that involves gathering user feedback, analyzing data, and making improvements based on insights. By continuously monitoring user behavior and adapting the design accordingly, UX designers can address pain points or areas of improvement, ensuring that the customer experience evolves over time.
In summary, UX design improves customer experience by prioritizing ease of use, intuitive interfaces, consistency, personalization, speed and performance, accessibility, emotional connection, and continuous improvement. By focusing on these aspects, UX designers create digital products that not only meet customer needs but also exceed their expectations, leading to enhanced satisfaction and loyalty.
UX designers utilize a variety of tools to aid in the design and development process. These tools help them understand user needs, visualize concepts, create prototypes, and test usability. Here are some commonly used tools in UX design:
- Wireframing and Prototyping Tools: Software like Sketch, Adobe XD, Figma, and Axure RP allow designers to create low-fidelity wireframes or high-fidelity interactive prototypes. These tools help visualize the structure and flow of the product before development.
- User Research Tools: Tools such as UserTesting, Optimal Workshop, and Hotjar enable designers to conduct user research through surveys, interviews, heatmaps, and usability testing. They provide insights into user behavior and preferences.
- Information Architecture Tools: Tools like Lucidchart or OmniGraffle assist in creating information architecture diagrams that define the organization and hierarchy of content within a digital product.
- Usability Testing Tools: Platforms like UsabilityHub or UserZoom facilitate remote or in-person usability testing by allowing designers to create tasks, gather feedback from users, and analyze results.
- Collaborative Design Tools: Platforms such as Miro or InVision Freehand enable designers to collaborate with team members remotely for brainstorming sessions, ideation workshops, or visual collaboration.
- Analytics Tools: Google Analytics or Mixpanel provide insights into user behavior on websites or apps, helping designers understand how users interact with their products and identify areas for improvement.
- Visual Design Tools: Software like Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator are used for creating visually appealing designs with attention to typography, color schemes, icons, and other visual elements.
- Prototyping Tools for Animation: Tools like Principle or Flinto allow designers to create animated transitions between screens in their prototypes for a more realistic user experience.
- Accessibility Evaluation Tools: Platforms such as WAVE Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool or Axe Browser Extensions help UX designers assess the accessibility of their designs and ensure compliance with accessibility standards.
- Project Management and Collaboration Tools: Tools like Trello, Asana, or Jira assist in project management, task tracking, and team collaboration, ensuring smooth communication and workflow between team members.
These tools are just a selection of the many available resources that UX designers can utilize to enhance their design process and create exceptional user experiences. The choice of tools often depends on personal preference, project requirements, and team collaboration dynamics.
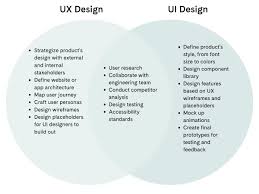
What is the difference between UI and UX design?
UI (User Interface) design and UX (User Experience) design are two distinct but interconnected disciplines in the field of digital design. While they are related, they focus on different aspects of the overall user experience.
UI design primarily deals with the visual and interactive elements of a digital product. It encompasses the look, feel, and layout of the interface that users interact with. UI designers are responsible for creating visually appealing designs that effectively communicate information and guide users through a seamless experience. They work on elements such as typography, color schemes, iconography, buttons, menus, and other visual components.
On the other hand, UX design focuses on the overall experience a user has while interacting with a product. It involves understanding user behaviors, needs, motivations, and goals to create an intuitive and satisfying experience. UX designers conduct research to gather insights about users’ preferences and pain points. They then use this information to inform decisions regarding navigation flows, information architecture, interaction patterns, and content strategy.
While UI design is more concerned with aesthetics and visual appeal, UX design is concerned with usability and user satisfaction. UX designers aim to create experiences that are efficient, enjoyable, and meet users’ expectations.
In summary:
– UI design focuses on the visual aspects of a digital product’s interface.
– UX design focuses on the overall user experience by considering usability, accessibility, and meeting user needs.
– UI design deals with elements like typography, color schemes, icons.
– UX design involves research to understand user behaviors and needs.
– UI is more about how things look; UX is about how things work.
Ultimately, both UI and UX design are essential for creating successful digital products. They work hand in hand to ensure that users have visually appealing interfaces that are intuitive to navigate and provide a positive overall experience.
How can I measure the success of my UX designs?
Measuring the success of UX designs is essential to understand how well your digital product or website is performing and to identify areas for improvement. Here are several key metrics and methods you can use to measure the success of your UX designs:
- User Testing: Conducting user testing sessions allows you to observe real users as they interact with your product. By collecting qualitative feedback and observing their behavior, you can gain valuable insights into usability issues, pain points, and areas where users may struggle.
- Usability Metrics: Usability metrics provide quantitative data on how users are interacting with your design. Metrics such as task success rate, time on task, error rates, and completion rates can help you gauge the efficiency and effectiveness of your UX design.
- Conversion Rates: If your digital product involves conversion actions like making a purchase or signing up for a service, tracking conversion rates can indicate the success of your UX design. Analyzing conversion funnels and identifying drop-off points can help optimize the user journey to improve conversions.
- User Satisfaction Surveys: Collecting feedback through surveys, such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) or Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) surveys, allows you to directly measure user satisfaction with your UX design. This provides insights into whether users find your product valuable and enjoyable.
- Heatmaps and Click Tracking: Heatmaps visually represent where users are clicking or spending the most time on a webpage or app screen. This data helps identify popular areas of interest or potential usability issues that need attention.
- Analytics Data: Analyzing quantitative data from tools like Google Analytics can provide insights into user behavior patterns, such as bounce rates, time on site, page views, and user flow. This data helps identify areas where users may be dropping off or experiencing difficulties.
- A/B Testing: A/B testing involves comparing two versions of a design to see which performs better in terms of user engagement or conversion rates. By testing different design elements or layouts, you can gather data to inform design decisions and optimize the user experience.
- Retention and Churn Rates: Tracking user retention and churn rates can indicate how successful your UX design is at keeping users engaged over time. High retention rates suggest that users find value in your product, while high churn rates may indicate issues with the user experience.
Remember that measuring the success of UX designs should be an ongoing process. Regularly analyzing data, gathering user feedback, and making iterative improvements based on insights will help ensure continuous enhancement of your UX design and overall product success.
How do I create a good user experience on mobile devices?
Creating a good user experience on mobile devices requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key principles and best practices to follow:
- Responsive Design: Ensure your website or app is responsive, meaning it adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and orientations. This ensures that users can access and interact with your content easily, regardless of the device they are using.
- Simplify Navigation: Mobile screens have limited space, so it’s important to simplify navigation by using clear and concise menus, icons, and buttons. Avoid cluttering the interface with too many options and prioritize the most important actions.
- Optimize Load Times: Mobile users expect fast-loading websites and apps. Optimize your assets (images, videos, etc.) for mobile devices to reduce file sizes without compromising quality. Minimize HTTP requests and leverage caching techniques to improve load times.
- Clear Call-to-Action (CTA): Make sure your CTAs are prominently displayed and easily tappable on mobile screens. Use contrasting colors, larger button sizes, and clear labels to guide users towards desired actions.
- Streamline Forms: Mobile forms should be simplified as much as possible. Minimize the number of required fields and consider using auto-fill or predictive text features to enhance input efficiency. Provide clear validation messages in real-time to help users complete forms correctly.
- Consistent Design Language: Maintain consistency across your mobile interface by using a unified design language that aligns with your brand identity. Consistency in typography, colors, icons, and spacing helps users navigate intuitively.
- Finger-Friendly Interactions: Design touch targets (buttons, links) with sufficient size and spacing to accommodate finger taps accurately without accidental clicks or frustration.
- Content Prioritization: Due to limited screen space on mobile devices, prioritize essential content above the fold (visible without scrolling). Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, and concise paragraphs for easy scanning and readability.
- Minimize User Input: Reduce the need for excessive typing on mobile devices. Leverage options like dropdown menus, checkboxes, and pre-filled information wherever possible to streamline user input.
- Test and Iterate: Regularly test your mobile experience across different devices, screen sizes, and operating systems to identify any usability issues or areas for improvement. Collect user feedback and iterate on your design based on real-world usage.
Remember, the goal is to create a seamless and enjoyable experience for users on mobile devices. By following these best practices and continuously optimizing your design based on user feedback, you can ensure a positive user experience that keeps users engaged with your mobile interface.
What trends should I be aware of when it comes to UX design?
When it comes to UX design, staying aware of the latest trends can help you create experiences that are both current and effective. Here are some trends to keep in mind:
- Microinteractions: Microinteractions are small, subtle animations or feedback that provide users with instant gratification and enhance their overall experience. They can be as simple as a button changing color when clicked or a loading spinner. Incorporating well-designed microinteractions can make interactions feel more engaging and responsive.
- Voice User Interface (VUI): With the rise of smart speakers and voice assistants, designing for voice interactions has become increasingly important. UX designers need to consider how users interact with products using voice commands and ensure that the experience is intuitive and conversational.
- Dark Mode: Dark mode has gained popularity due to its ability to reduce eye strain, save battery life on mobile devices, and provide a sleek aesthetic. Designing interfaces with dark mode options allows users to choose their preferred visual experience.
- Minimalism and Simplified Interfaces: Minimalistic design focuses on removing unnecessary elements while emphasizing clarity and simplicity. By decluttering interfaces, designers can create more intuitive experiences that allow users to focus on the essential content or tasks.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): As AR and VR technologies continue to advance, integrating them into UX design can offer immersive experiences for users. From virtual tours to interactive product demonstrations, these technologies have the potential to revolutionize how users engage with digital products.
- Personalization: Users now expect personalized experiences tailored to their preferences and needs. By leveraging user data and employing techniques like machine learning, UX designers can create customized interfaces that adapt based on user behavior, location, or previous interactions.
- Gestures and Swipe Navigation: With touchscreens becoming ubiquitous, gesture-based navigation has become more prevalent in UX design. Incorporating intuitive swipe gestures allows for fluid interaction patterns that are familiar to users and enhance their overall experience.
- Inclusive Design: Inclusive design focuses on creating experiences that are accessible to users of all abilities. Designers need to consider factors such as color contrasts, font sizes, alternative text for images, and keyboard navigation to ensure that their products can be used by a diverse range of users.
Remember, while trends can provide inspiration and guidance, it’s essential to evaluate their suitability for your specific project and target audience. Striking a balance between incorporating trends and maintaining usability is key to creating successful user experiences.
Tags :
accessibility,
apps,
behaviors,
clear information hierarchy,
continuous evaluation and improvement,
critical component,
delight users,
devices,
digital products,
ease of navigation,
efficient task completion,
emotions perceptions behaviors when interacting with a digital interface,
empathy,
engaging,
enhancing user satisfaction,
highly functional,
interaction between users and a product or system,
intuitive,
keep them coming back,
meaningful and enjoyable,
meticulous planning,
mobile responsiveness,
needs,
pain points,
preferences of users,
prototyping,
research,
responsive design,
seamless digital experiences,
seamless experiences,
smooth and effortless interactions,
structure and flow of a product,
successful websites,
testing,
usability,
usability testing,
user experience design,
user research,
visually appealing,
wireframing